CBSE Class 11 Physics Notes Chapter 4 Motion in a Plane

CBSE Class 11 Physics Notes Chapter 4 Motion in a Plane
Class 11 Physics is one of the most important subjects for students preparing for board exams and competitive exams like JEE and NEET. It helps in building a strong base for advanced concepts in Class 12. Each chapter in the syllabus carries weight in exams, and understanding every topic clearly is very important to score well. Chapter 4, Motion in a Plane, is one such topic that introduces students to the concepts of two-dimensional motion. It explains vectors, projectile motion, and uniform circular motion, which form the base for many higher-level topics in Physics.
In this article, students will find well-organised motion in a plane class 11 notes that cover all the key formulas, definitions, and solved examples in an easy-to-understand way. These class 11 physics chapter 4 notes will help students revise quickly before exams and strengthen their conceptual clarity. So, if you are looking for complete and clear motion in plane class 11 notes, you are at the right place.
Check Out: Class 11th Books
Motion in a Plane Class 11 Notes
Go through the class 11 physics ch 4 notes here:-
CBSE Class 11 Physics Notes Chapter 4
Scalars and Vectors
A distinct number can be used to characterise some quantities. For instance, one number can be used to represent mass, time, distance, and speed. We refer to these as scalar quantities. One piece of knowledge is insufficient to explain to someone how to move from one place to another. It need both displacement and distance to properly explain this. Vectors are quantities that need to be measured in both magnitude and direction in order to completely characterise a situation. Vectors include things like velocity and displacement.
Addition, subtraction and scalar multiplication of vectors:
Consider two vectors as follows:

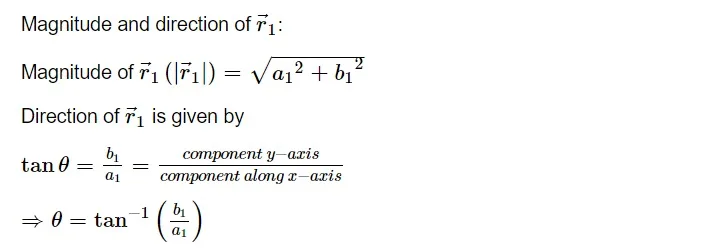
Parallel vectors
If and only if two vectors have the same direction, they are said to be parallel. Any vector multiplied by a scalar yields a vector that is parallel to the original vector.
Equality of vectors
If the corresponding magnitudes and directions of two vectors, which reflect two values of the same physical quantity, are the same, then they are said to be equal.
Addition of vectors
The solution is known as the resultant when two or more vectors are combined. When two vectors are combined, the outcome is equal to the first vector immediately after the second vector.

Subtraction of vectors
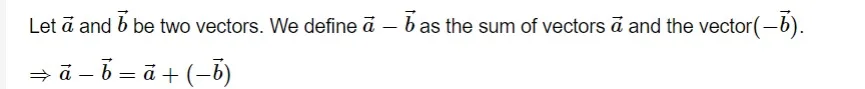
Zero vector

Resolution of vectors

Check Out: CBSE Question Bank Class 11 Physics
Motion In 2D (PLANE)
Position vector and Displacement


Average velocity
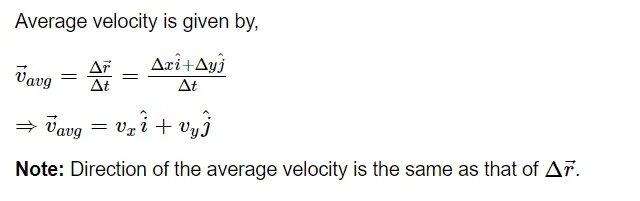
Instantaneous velocity
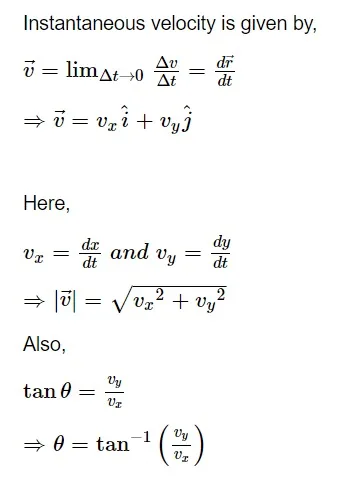
PROJECTILE MOTION
A particle moves in both horizontal and vertical directions simultaneously when it is propelled obliquely near the earth's surface. Projectile motion is the term used to describe the motion of such a particle.
Here, a particle is projected at an angle with an initial velocity ‘u’.
Considering the projectile motion given in the diagram above, let us calculate the following:
(a) time taken to reach A from O
(b) horizontal distance covered (OA)
(c) maximum height reached during the motion
(d) velocity at any time ‘t’ during the motion
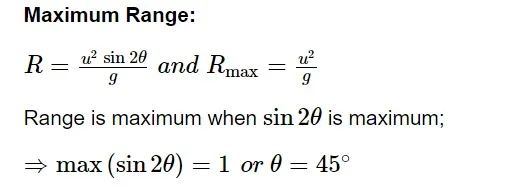
Equation of trajectory
The path the body follows is referred to as a trajectory. After removing time, we should establish the relationship between y and x in order to calculate the trajectory.
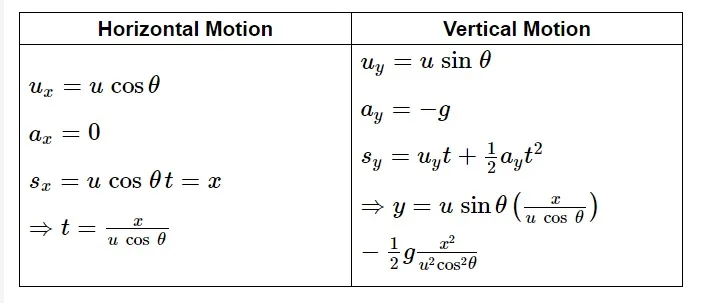
Relative Motion
Relativity is a very common term. In physics, we use relativity very oftenly.
Case I: If you are observing a car moving on a straight road, then you say that the velocity of car is 20m/s; which means that velocity of car relative to you is 20m/s; or, velocity of car relative to the ground is 20m/s (as you are standing on the ground.
Case II: If you go inside this car and observe, you would find that the car is at rest while the road is moving backwards. Then, you would say, the velocity of the car relative to the car is 0m/s.

Check Out: Class 11th Question Banks
CBSE Class 11 Physics Notes Chapter 4 PDF
Physics 11 Motion on a Plane is a crucial chapter. As a result, we are offering revision study materials to aid students in quickly revising the Motion in a Plane chapter. We have included the numerous significant questions and answers from Motion in a Plane, which are necessary for students to learn, in our review study.
CBSE Class 11 Physics Notes Chapter 4 PDF
Summary of Class 11 Physics Chapter 4
Check out the quick summary of the Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 Motion in a Plane:-
-
Scalars and Vectors: Scalars have only magnitude (like speed, distance), while vectors have both magnitude and direction (like velocity, displacement).
-
Vector Representation: Vectors can be represented using arrows, where the length shows magnitude and the direction of the arrow shows the direction of the quantity.
-
Addition and Subtraction of Vectors: Vectors can be added or subtracted using the triangle law or parallelogram law.
-
Resolution of Vectors: Any vector can be broken into two components, one along the x-axis and the other along the y-axis.
-
Projectile Motion: It is the motion of an object thrown into the air, making a curved path (parabola). Examples include a ball being thrown or a bullet being fired.
-
Uniform Circular Motion: When an object moves in a circle at a constant speed, its direction changes continuously, which means it has acceleration (centripetal acceleration).
-
Relative Velocity: It helps to find how fast one object is moving with respect to another object.
How to Use CBSE Class 11 Physics Notes Chapter 4?
The motion in a plane class 11 notes are made to help students understand the chapter easily and revise it quickly before exams:-
1. Read the Notes After Each Topic: After finishing every topic from your textbook, read the motion in a plane notes. It helps in revising what you just studied and clears small doubts.
2. Mark Important Formulas: While going through the motion in plane class 11 notes, highlight or note down the key formulas for projectile motion, vectors, and circular motion. These are often asked in exams.
3. Practise Questions Regularly: Use the class 11 motion in a plane notes to solve examples and numerical problems. Regular practice makes you confident for both school and entrance exams.
4. Revise Before Tests: Go through these class 11 physics chapter 4 notes before your tests to revise all the main points quickly. It saves time and helps you remember important concepts.
5. Use for Quick Reference: Whenever you get confused about any concept, take a quick look at the motion in a plane class 11 notes. They are short, clear, and easy to understand.
Read More: NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Physics Chapter 4
CBSE Class 11 Physics Notes Chapter 4 FAQs
1. What is meant by motion in a plane?
Motion in a plane means motion that takes place in two dimensions, like along the x and y axes.
2. What is the difference between scalar and vector quantities?
Scalar quantities have only magnitude, while vector quantities have both magnitude and direction.
3. What are examples of vector quantities?
Displacement, velocity, acceleration, and force are all examples of vectors.
4. What is projectile motion?
Projectile motion is the curved path followed by an object thrown in the air, like a ball or bullet.
5. What are the two components of projectile motion?
The two components are horizontal motion (constant velocity) and vertical motion (under gravity).










